A surge tank, also known as a buffer tank, is a vital component designed to withstand pressure and maintain a sealed state. Widely utilized in various air compression systems, it serves as a functional product capable of automatically stabilizing pressure, thereby reducing system energy consumption. Let's delve deeper into the structure, function, and working principles of surge tanks.
1. Function of Surge Tanks
The primary function of a surge tank is to mitigate pressure fluctuations within a system, ensuring smoother operation. Its buffering performance is primarily achieved through the compression of air within the tank. Currently, there are two common types of surge tanks in the market: diaphragm and bladder tanks, both extensively employed in central air conditioning, boilers, water heaters, variable frequency drives, and constant pressure water supply equipment. During system operation, a surge tank effectively eliminates pressure fluctuations, alleviates water hammer effects, stabilizes water supply pressure, and reduces the energy consumption associated with frequent pump startups and shutdowns.
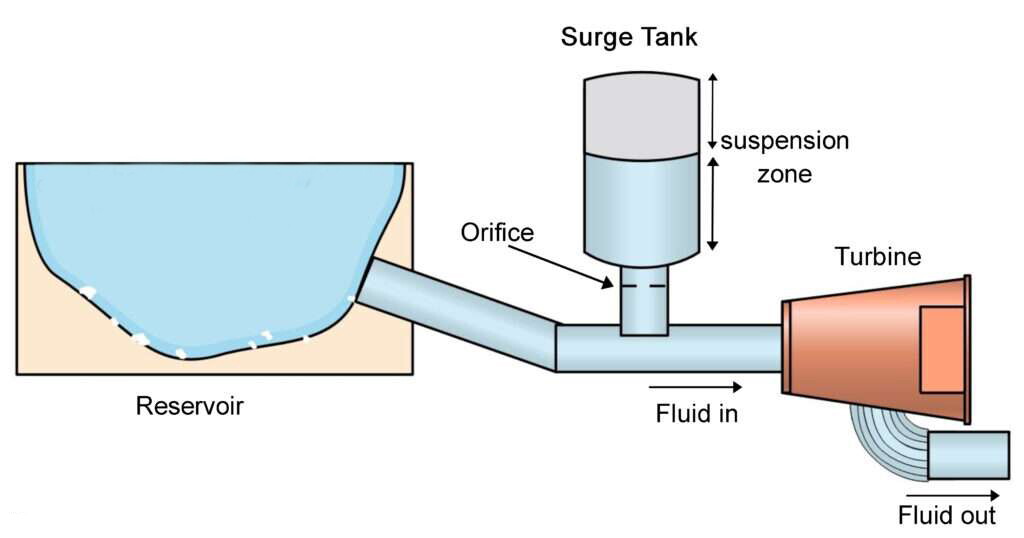
2. Structure and Working Principles of Surge Tanks
Surge tanks capitalize on the minimal compressibility of liquids, storing liquid within the tank through external force. When the external force dissipates, the compressed gas expands, pushing the liquid out. Its main components include valve covers, inflation ports, bladders, carbon steel tank bodies, and flange discs. When connected to a water system, the surge tank acts as an energy accumulator. If the system water pressure exceeds the pressure of the gas between the tank body and bladder, water is forced into the bladder until a new equilibrium is reached, compressing the gas and increasing system pressure. Conversely, if the system water pressure falls below the gas pressure within the bladder, water is expelled from the bladder, replenishing the system until pressure equilibrium is restored. Through this mechanism, surge tanks effectively regulate pressure fluctuations, ensuring system stability and reliability.
In addition to the fundamental structure and principles, modern surge tanks may also be equipped with intelligent control systems, utilizing sensors to monitor system pressure in real-time. This allows for more precise adjustment of gas pressure within the surge tank, enhancing system stability and efficiency.
As a crucial component in various industrial and domestic applications, surge tanks play a significant role. Through their ingenious design and operating principles, surge tanks effectively stabilize system pressure, reduce energy consumption, and enhance operational efficiency and reliability. With ongoing technological advancements and expanding application domains, surge tanks will continue to serve as indispensable components, providing stable and reliable technical support across industries.

 English
English Español
Español русский
русский