In the realm of oil and gas production, three-phase separators emerge as indispensable equipment, instrumental in segregating mixtures of crude oil, natural gas, and water. These separators play pivotal role in the development process of oil and gas fields is paramount, directly impacting production efficiency and the maximization of resource utilization.
Stages of Three-Phase Separator Application
Three-phase separators play a pivotal role in the production process within oil and gas fields, typically involving several crucial application stages:
During the initial stages of production, a blend of fluids containing crude oil, natural gas, and water is extracted from oil wells. At this juncture, wellhead separators come into play, serving to preliminarily separate these three phases, thereby ensuring that each component—crude oil, natural gas, and water—enters subsequent processing systems individually.
Production Facility Separation:
As production scales up, larger-scale three-phase separation equipment becomes necessary to handle mixed fluids from multiple wells efficiently. This ensures effective separation of different components before they are directed to processing facilities.
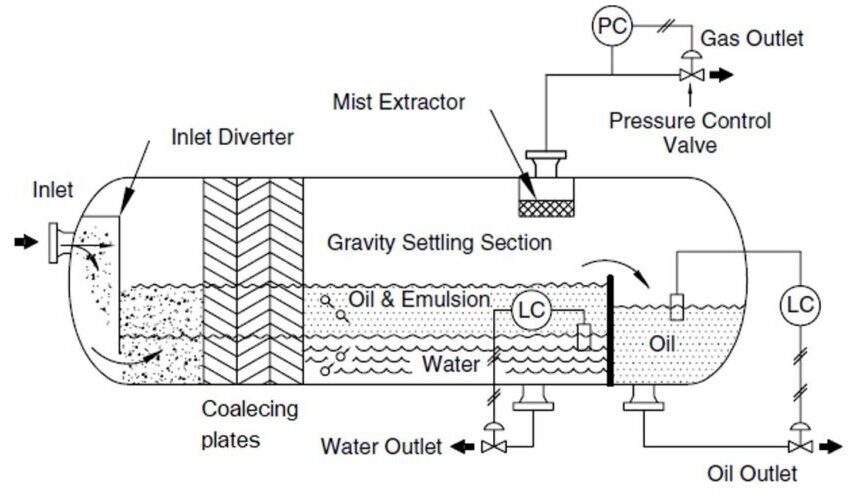
Internal Structure of Three-Phase Separators
The internal architecture of three-phase separators encompasses various components, including inlet mechanisms, rectifiers, coalescing sections (such as corrugated plate assemblies), water settling areas, oil settling segments, among others:
- Inlet: The inlet serves as the entry point for mixed fluids into the three-phase separator, either from the wellhead or production facility.
- Separation Chamber: The separation chamber stands as the nucleus of the three-phase separator, leveraging principles like gravity separation, buoyancy, and centrifugal force to effectively segregate crude oil, natural gas, and water.
- Oil Outlet: Extracted crude oil exits the separator through the designated oil outlet, ready for further processing.
- Gas Outlet: Natural gas is drawn out from the separation chamber and typically directed toward gas processing systems.
- Water Outlet: Water is extracted from the separation chamber, often necessitating additional treatment or reinjection into reservoirs.
- Control Valves and Instruments: These components play a pivotal role in monitoring and regulating the operational status of the three-phase separator, ensuring optimal separation efficiency.
Operational Principles of Three-Phase Separators
The operational principles of three-phase separators hinge upon the density and relative motion of different components. Through the strategic application of centrifugal force, buoyancy, and gravity, these separators effectively partition mixed fluids into their constituent elements—crude oil, natural gas, and water—thereby ensuring efficient production and processing within oil fields.
Selecting the Appropriate Three-Phase Separator
When selecting a three-phase separator, a multitude of factors must be taken into account:
- Flow Rate and Pressure: Choose a separator size and operational parameters commensurate with the production rate and requirements of the oil field.
- Separation Efficiency: Different designs and models offer varying separation efficiencies. Opt for a separator that aligns with the composition of oil and gas components for optimal separation.
- Material and Corrosion Resistance: Consider the chemical composition of fluids and select materials resistant to corrosion to enhance the equipment's longevity.
- Operational Convenience and Maintenance: Prioritize designs that are user-friendly and easy to maintain, thus minimizing operational costs.
In summation, three-phase separators constitute an integral component of the oil and gas production process. By adeptly segregating mixtures of crude oil, natural gas, and water, they bolster production efficiency, curtail operating costs, and mitigate environmental risks. Selecting the appropriate three-phase separator is paramount for the development of oil and gas fields, necessitating a comprehensive evaluation of various factors to realize optimal production and processing outcomes.
