Pressure vessels play an indispensable role in various industrial applications, facilitating the storage and transportation of gases and liquids under high pressures. However, over time and due to various external factors, pressure vessels may develop cracks, which can pose significant risks to both operational safety and productivity. This article aims to delve into the causes of pressure vessel cracking, the hazards it presents, and the corresponding mitigation measures, providing comprehensive insights for industries reliant on such equipment.
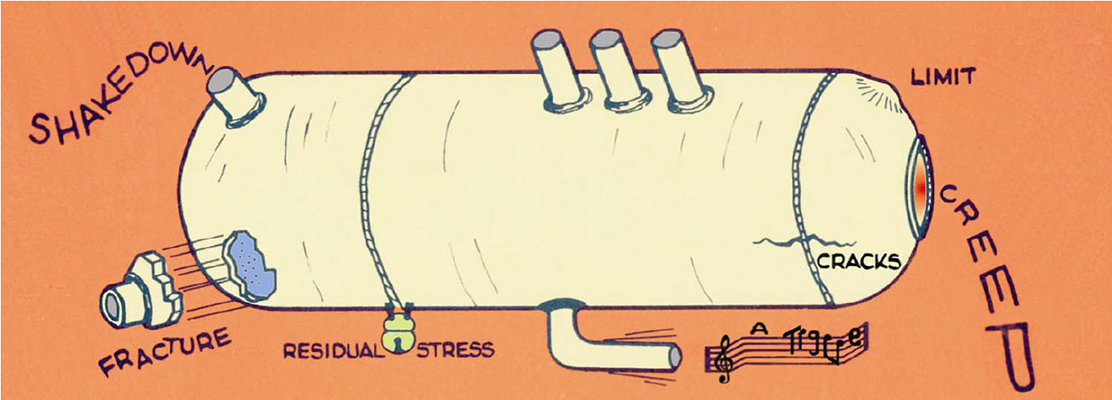
Causes of Cracked Pressure Vessel
The emergence of cracks in pressure vessels is often the result of multiple factors:
- Material Quality Issues: Defects in manufacturing materials or inadequate quality control measures may lead to the presence of microdefects in the vessel walls, which can propagate into cracks over prolonged usage.
- Corrosion and Wear: Prolonged exposure to harsh environments can cause corrosion and wear on pressure vessel surfaces, resulting in thinning walls or the development of microscopic cracks.
- Excessive Pressure and Temperature: Under specific operating conditions, such as sudden pressure surges or temperature fluctuations, the stress on the vessel walls may exceed design limits, leading to stress-induced cracking.
Analysis of the Major Hazards
The occurrence of cracks in pressure vessels can lead to multifaceted hazards:
- Fragmentation Hazard: Upon rupture, high-velocity gas release exerts a reactive force, causing the vessel to fragment and potentially hurl shards, posing risks of injury to personnel and equipment damage.
- Combustion and Explosion Hazard: If the vessel contains flammable substances, cracks may allow for the mixing of these substances with air, leading to fires or explosions that endanger lives and property in the vicinity.
- Shockwave Hazard: The release of energy upon vessel rupture generates shockwaves capable of damaging surrounding structures and equipment, resulting in severe casualties and environmental damage.
- Toxic Hazard: Cracks in vessels containing toxic substances may result in the release of harmful gases, posing serious health risks to nearby individuals and environmental ecosystems.
Prevention Measures
To mitigate the occurrence of pressure vessel cracking and its associated hazards, the following measures are recommended:
- Enhanced Quality Control and Oversight: Strengthen quality control measures during manufacturing to ensure material quality meets standards and enforce strict regulatory oversight to minimize defect rates.
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Implement routine inspections and maintenance protocols for pressure vessels, including external checks and internal flaw detection, to promptly identify and rectify potential issues, thereby extending vessel lifespan.
- Prudent Usage and Management: Exercise caution in selecting operating environments and conditions for pressure vessels, avoiding extreme conditions to ensure vessels operate within safe parameters.
- Personnel Training and Safety Awareness: Provide comprehensive safety training for personnel, enhancing their safety awareness and emergency response capabilities to effectively mitigate incidents should they occur.
Pressure vessel cracking is a prevalent concern in industrial settings, posing serious risks to safety and efficiency. Through thorough analysis of causes and hazards, along with the implementation of effective mitigation measures, industries can bolster the safety and reliability of pressure vessel operations, protecting both processes and personnel. Additionally, enhanced regulations and technological advancements play vital roles in preventing and reducing instances of pressure vessel cracking.
