Heat exchangers are indispensable components in both industrial processes and household systems, with U-tube heat exchangers emerging as a prominent and versatile option. This article aims to delve deeper into the definition, advantages, and comparative analysis of U-tube heat exchangers against other shell-and-tube counterparts.
I. Introduction to U-Tube Heat Exchangers
U-tube heat exchangers belong to the category of shell-and-tube heat exchangers, characterized by fixed tube sheets, a floating head, U-shaped tubes, sliding tube sheets, filler functions, and casings. Tailored to specific requirements such as medium properties, pressure, temperature, and contamination levels, the design encompasses suitable tube sheet-to-shell connections, shapes, and heat transfer conditions.
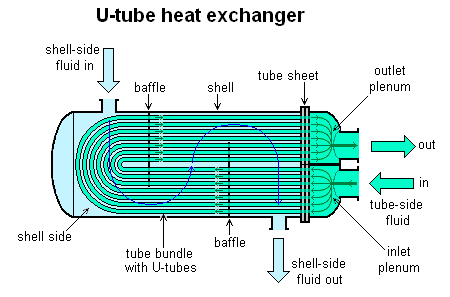
II. Advantages of U-Tube Heat Exchangers
- Flexibility in Tube Bundles: The ability of tubes to expand and contract independently ensures excellent thermal compensation without inducing thermal stresses due to temperature differentials.
- Enhanced Performance: Employing a double-row tube configuration, U-tube heat exchangers exhibit robust pressure-bearing capacities and superior heat transfer coefficients, resulting in heightened heat transfer efficiency.
- Ease of Maintenance and Cleaning: Removable tube bundles facilitate convenient maintenance and cleaning, contributing to a straightforward structure and cost-effectiveness.
- Space Efficiency: Compact design minimizes spatial footprint, making U-tube heat exchangers suitable for applications where space is limited.
- Superior Hydraulic Characteristics: Low flow resistance translates to significant energy savings, making them environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
- Improved Heat Transfer Efficiency: Reduced heat transfer area by approximately 40% to 60% compared to conventional counterparts.
- Reduced Condensate Water Temperature: Elimination of drainage devices with a simple piping system leads to lower heat dissipation losses.
III. Comparison with Other Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchangers
U-tube heat exchangers differ from other shell-and-tube variants primarily due to their U-shaped tube configuration, leading to the following distinctions:
- Tube Structure: U-tube heat exchangers feature tubes bent into a U-shape, allowing fluid inlet and outlet on opposite sides of the same end, enabling free expansion and contraction to address thermal compensation requirements.
- Flow Dynamics: Both internal and external fluids flow in parallel and counterflow within U-tube heat exchangers.
- Connection Methods: Double-row tube sheets are commonly connected using a liquid collecting shell, while a condensing oil shell prevents gas (liquid) leakage.
- Port Arrangement: Condensing oil shells are equipped with empty and cleaning ports for the timely discharge of leaked gas (liquid).
U-tube heat exchangers, renowned for their efficiency, versatility, and compact design, play pivotal roles across various industrial and domestic applications. Their distinct features and benefits position them as preferred solutions, offering reliable heat transfer solutions while optimizing resource utilization and operational efficiency.
